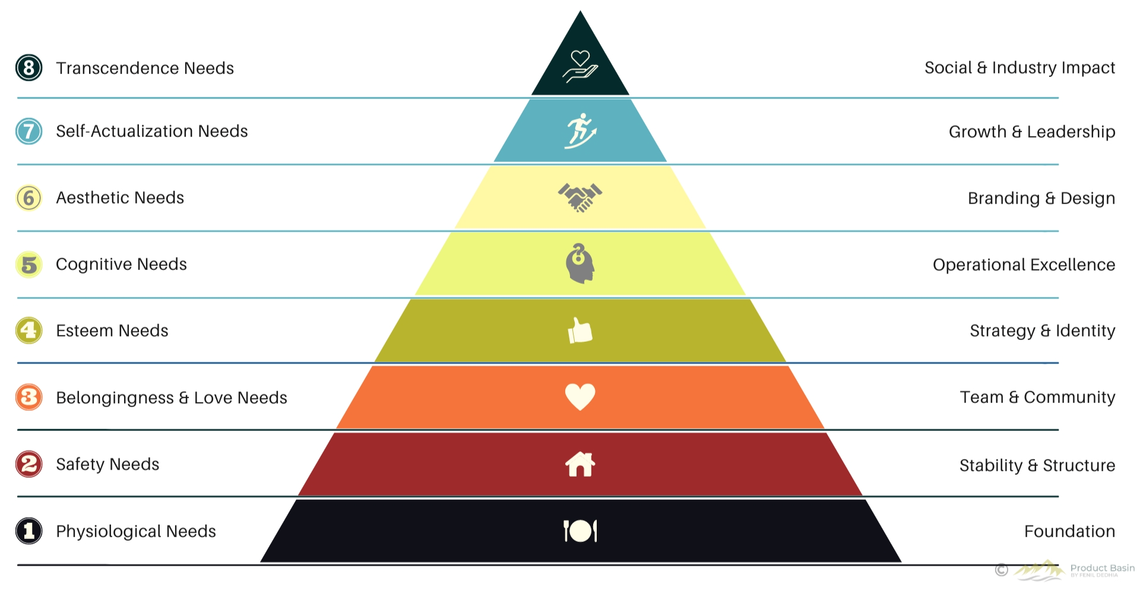
Applying Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs to a Software Business
In the world of software business, it's easy to lose sight of the big picture. Whether you're part of an early-stage startup, a growing mid-size company, or an established enterprise, the challenge remains: How do you prioritize your focus and resources to drive sustainable growth?
As someone who's been in the trenches of both early-stage startups and larger organizations, I've witnessed firsthand the struggles teams face in balancing immediate needs with long-term needs. I've noticed how easy it is for leaders and individual contributors alike to get caught up in day-to-day operations, and the big-picture thinking often gets lost in the shuffle. Unknowingly, most companies tend to hyper-focus on one or two areas; this often leads to the neglect of the broader spectrum of needs that a thriving company must address.
That's why I've created this adaptation of Maslow's Hierarchy for software businesses. I trust it can serve as the compass I wish I'd had throughout my career.
Whether you're a founder, a team lead, or an ambitious IC, this framework offers you a clear way to assess your company's current position, identify potential gaps, and navigate the terrain of scaling a software business.
The goal isn't to race to the top of the hierarchy. It’s to build a resilient company capable of thriving at every level. From Physiological needs to Transcendence needs, the journey of the software business reflects rising human needs, each building upon and starting from the previous one to reach new heights of impact.
Navigating the Hierarchy: Key Considerations
The Non-Linear Nature of Growth
While the hierarchy presents a linear progression, the hierarchy is more fluid in practice. Startups often juggle multiple levels simultaneously, adapting to challenges as they arise. The framework should be used as a guide, not be interpreted as a rigid rulebook or an attempt to race to the top. It's not about racing to the top of the hierarchy. It's about building a resilient company that can thrive at every level.
Reinforcing the Foundation
The lower-level needs do not become irrelevant as the software company grows. Even as companies grow, they must continually reinforce their foundation. The framework suggests where the primary focus might shift.
Accommodating Disruptive Innovations
Disruptive innovations can accelerate your journey through the hierarchy, but be cautious. While rapid advancement is possible, sustainable success often requires backfilling skipped steps. Use the model to identify and address any gaps in your foundation as you grow.
Pivoting with Purpose
Pivots are a natural part of the startup journey. When facing a pivot, use this hierarchy as a tool for reassessment. Evaluate which levels need attention in light of your new direction, ensuring you’re rebuilding from a solid foundation while adapting to new circumstances.
Let's dive in.
Maslow’s Hierarchy for a Software Business
Foundation (Physiological Needs)
- Vision: Establishing a clear and inspiring long-term goal that guides the company's direction. Vision could evolve with the company, but at this stage sets the initial direction of the company.
- Basic Infrastructure: Essential resources like technology, facilities, and utilities.
Structure & Stability (Safety Needs)
- Funding: Securing initial capital to cover basic expenses such as salaries, office space, and equipment.
- Initial Resources: Setting up foundational processes, team members, and systems necessary for day-to-day operations.
- Company Values & Culture: Defining and instilling the core values and culture that guide behavior and decision-making within the company.
- Legal and Compliance: Ensuring the business is legally established and compliant with relevant regulations.
- Minimum Viable Product (MVP): Developing the most basic version of your software that can be released to early adopters. The MVP is a critical focus area when you're early-stage. As the team and product evolve, the growth-stage focus naturally shifts towards Innovation and Continuous Development (part of Self-Actualization needs). This progression involves increased investment in R&D efforts and experimentation with new POCs and MVPs to capitalize on emerging market opportunities and technological inflections.
Team & Community (Belongingness and Love Needs)
- Competent Employees: Hiring more skilled and motivated team members who fit the company culture. Competent employees are the backbone of any successful team. They boost morale, drive productivity, and fuel innovation. Hiring wisely isn't just about skills—it's about building a culture of excellence that pushes your business forward.
- BTW, hiring is the most underrated business strategy. What separates the top 10% of companies from the rest isn't their technology or processes—it's often their hiring standards and culture. A-players naturally attract and hire other A-players, creating a virtuous cycle. The greatest differentiators in high-performing teams are curiosity and high agency. Unfortunately, most business problems in 90% of organizations are rooted in People and often go under the radar.
- Team Building: Fostering a sense of belonging and collaboration among employees.
- Early Adopters: Gaining a group of initial users who believe in your product and provide valuable feedback.
- Partnerships: Establishing initial strategic partnerships to enhance your product offering or market reach.
Strategic Execution & Identity (Esteem Needs)
- Strategic Planning: Developing detailed plans to achieve the vision, including market analysis and competitive positioning. This includes clear guidance on how the business might differentiate itself from competitors while outlining what they will NOT pursue. Establishing a strategy involves setting clear, measurable objectives and devising actionable strategies to meet them. By establishing a solid strategic framework, businesses can ensure that all efforts are directed towards long-term success and sustainability. A crucial yet often underrated component of strategic planning is setting a high bar for hiring. By rigorously selecting top talent that aligns with the company’s vision and culture, businesses can build a strong, capable team that drives innovation and executes the strategic plan effectively.
- Execution: Efficiently implementing strategies through effective processes and performance management. This will involve optimizing operations to ensure maximum efficiency and setting key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress and achieve goals. In practice, effective execution is about turning strategic plans into actionable steps that drive the business forward, knowing that all team members are aligned and working towards common objectives.
- Product-Market Fit: Validating that your software solves a real problem and meets market demand.
- Brand Identity: Developing a unique and recognizable brand that resonates with your target audience.
Operational Excellence (Cognitive Needs)
- Data-Informed Decision Making: Implementing analytics and metrics to inform product development and business strategies.
- Quality and Customer Satisfaction: Ensuring high-quality products or services that delight customers. This has to be done through the establishment of strict standards and quality assurance procedures in order to preserve consistency and reliability. Gathering and analyzing customer feedback helps identify areas for improvement and ensures that the business meets or exceeds customer expectations. Continuous improvement is key, with regular reviews and enhancements to processes that uphold the highest standards of quality.
- Sustainable Revenue Streams: Achieving consistent profitability and financial health. Developing sustainable revenue streams involves creating strategies that generate consistent income and ensure profitability. This involves careful financial planning to forecast and manage resources effectively, as well as implementing cost control measures to maximize profitability. By focusing on sustainable revenue generation, businesses can achieve financial stability and support ongoing growth and development.
Branding & Reputation (Aesthetic Needs)
- Customer Experience (CX) Design: Creating intuitive and delightful touchpoints for the customers. This includes enhancing the software interfaces to be more intuitive, more aesthetically pleasing, and more aligned with branding guidelines. By prioritizing CX design, companies can enhance user satisfaction, increase customer loyalty, and differentiate themselves in the market.
- Reputation: Building a positive brand image and gaining respect in the industry. This involves consistently delivering high-quality products or services, engaging in ethical business practices, and maintaining transparent communication with stakeholders. A strong reputation can attract customers, partners, and top talent, all of which contribute to the company’s overall success and credibility.
- Risk Management: Establishing robust processes for mitigating risks and ensuring long-term stability. This includes identifying potential threats to the business, assessing their impact, and implementing strategies to minimize or eliminate them. Effective risk management helps protect the company’s assets, reputation, and financial health, providing a secure foundation for future growth and development.
Growth & Leadership Development (Self-Actualization Needs)
- Scalability: Developing systems and processes that allow for rapid, sustainable growth.
- Innovation and Continuous Development: Encouraging creativity and continuous improvement to stay ahead in the market. Innovation embraces a new ideas environment. It may include different levels of investments in research and development, adaptation of new technologies, and encouragement of employees towards out-of-the-box thinking. Effective R&D efforts will keep your company adaptable and responsive to changing market conditions, driving progress and growth.
- Growth: Expanding the business through new markets, products, or services. If you’re a product company, this often involves adopting new growth models such as Product-Led Growth (PLG) and Product-Led Sales (PLS). PLG leverages the product itself to drive customer acquisition, retention, and expansion, reducing the need for traditional marketing and sales efforts. This approach includes offering free trials, freemium models, and optimizing user onboarding to highlight the product's value. PLS, on the other hand, integrates traditional sales strategies with product-led tactics, ensuring that both self-serve and sales-led methods are used to convert and expand customer relationships. Such growth models help companies achieve scalable and sustainable growth by focusing on user experience and engagement from the start.
- Leadership Development: Cultivating future leaders within the organization. This involves identifying and nurturing talent, providing opportunities for professional development, and fostering a culture of mentorship and support. Effective leadership development ensures that the company is well-equipped to navigate future challenges and seize opportunities.
Social & Industry Impact (Transcendence Needs)
- Corporate Social Responsibility: Contributing to societal well-being and sustainability.
- Mentorship and Knowledge Sharing: Investing in the broader community and industry by sharing knowledge and supporting other businesses or startups.
- Innovation Leadership: Positioning the company as a thought leader and innovator in its field. By embracing this role, companies can influence the direction of their industry, attract top talent, and create lasting legacies that extend far beyond their immediate products or services.
- Industry Transformation: Using your success and influence to drive positive change in your industry or beyond.
Closing Thoughts
I want you to think of this adaptation of Maslow's Hierarchy as your compass for navigating your company's growth. I've simplified a complex journey here, and your business will undoubtedly chart its own unique path.
As you apply this model, embrace its flexibility. Your business may find itself focusing on multiple levels simultaneously or revisiting earlier stages as you grow; this is not only normal but can be a sign of a dynamic, responsive organization.
Remember, the goal isn't to race to the top of the hierarchy. It’s to build a resilient company capable of thriving at every level. Even as our companies grow, we must continually reinforce their foundation.
The framework suggests where the primary focus might shift.
By addressing the needs at each stage, you're creating a rock-solid foundation for sustainable growth.

Member discussion